C RWG
O
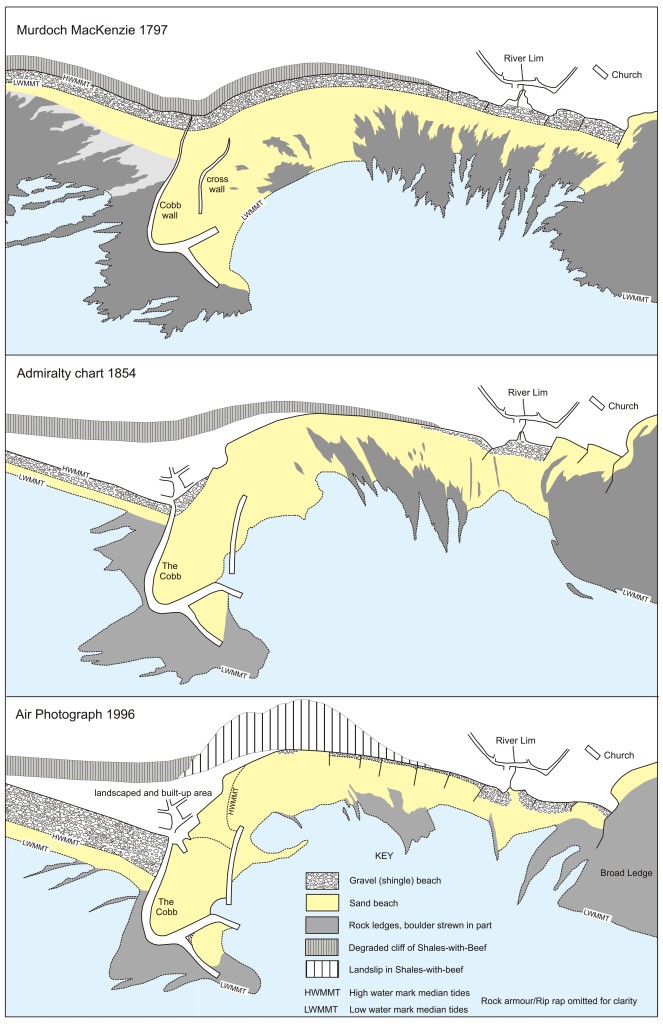
Early drawings and accounts show that the Cobb harbour wall was not connected to the shore until the 18th century. A low causeway was built to link it to the land when a new wall was constructed in 1756. With time, this wall and the causeway were increased in height to produce the present-day wall, the landward end of which was last raised in 1939 to provide year-round protection for an air-sea rescue facility. These changes to the Cobb wall have interfered with the natural west-to-east longshore drift of beach shingle. This has resulted in a steady accumulation of shingle to the west of the wall and the consequential loss of shingle from the town beach. The removal of the protective belt of shingle from the foot of this cliff probably encouraged its landslides.
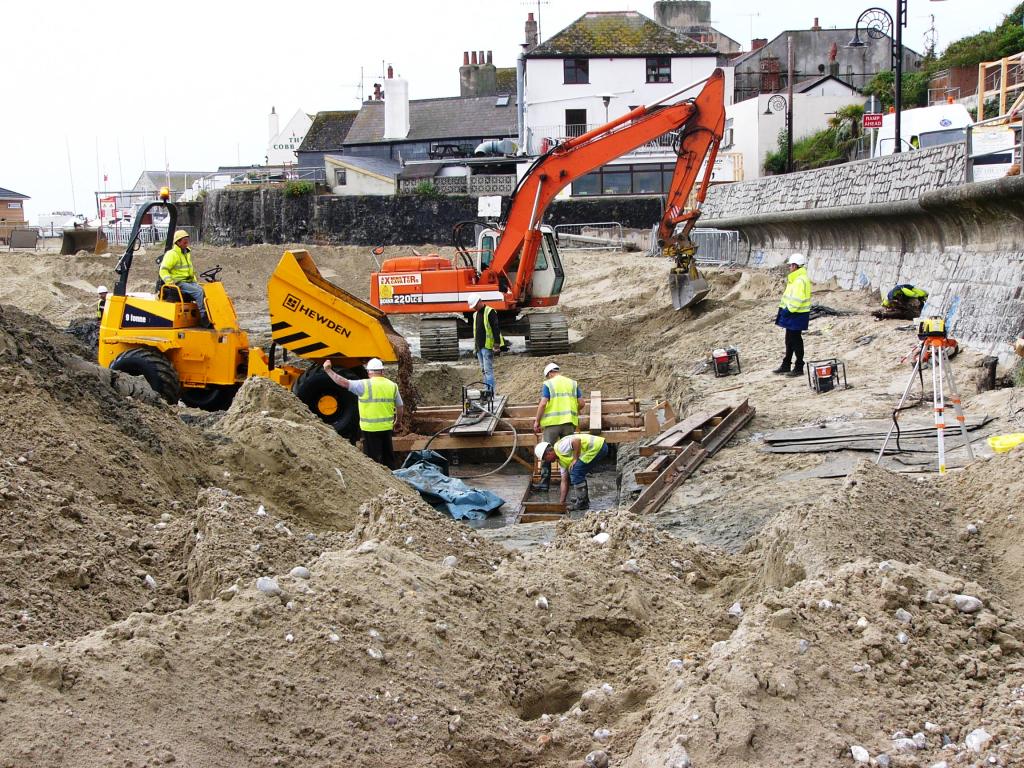

Remedial engineering works at Lyme Regis that were designed to stabilise shallow-seated landslides included the construction of a new sea wall. This fulfils the dual purpose of replacing a sea wall that had become undermined by marine erosion and acting as a toe weight to prevent future landsliding.
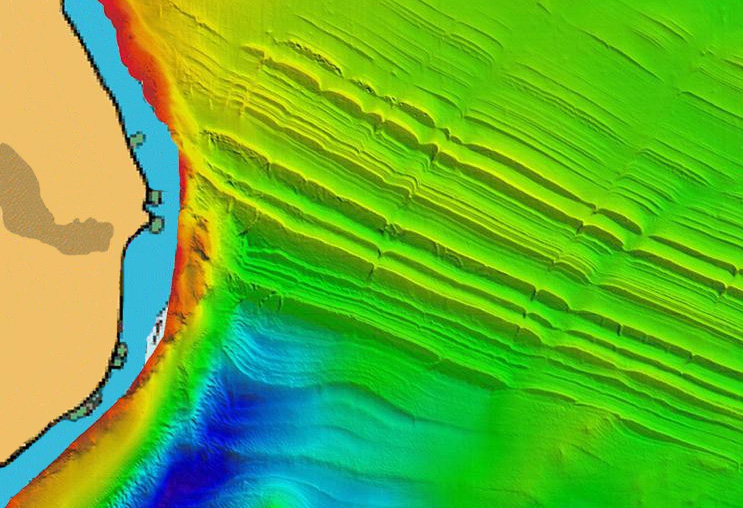
The shape of coastlines and the differential rates at which they erode are intimately associated with the geology. This is especially well displayed on the English south coast where Triassic to Tertiary strata with low (mostly < 2° ) dips crop out in long sections of unbroken cliff. This deceptively simple structure is complicated by faults that mostly strike almost normal to the coastline, and faults that are subparallel to the coastline. These have a marked influence on the shape of the coastline. The former are almost all overlain by valleys that are infilled with Quaternary sediments. The latter are poorly known except in those intertidal areas where they are not covered by beach deposits, and in a few nearshore areas where sonar surveys have been carried out. In Portland Bay, recent surveys have shown that ledges that crop out on the sea bed can be matched in remarkable detail with the stratigraphy of Kimmeridge Clay proved in onshore boreholes. Digitised multibeam sidescan sonar image of the offshore area adjacent to Grove Point, Isle of Portland made for the Channel Coast Observatory (CCO). Reproduced courtesy and copyright of the CCO (www.cco.org.uk).
C RWG
O